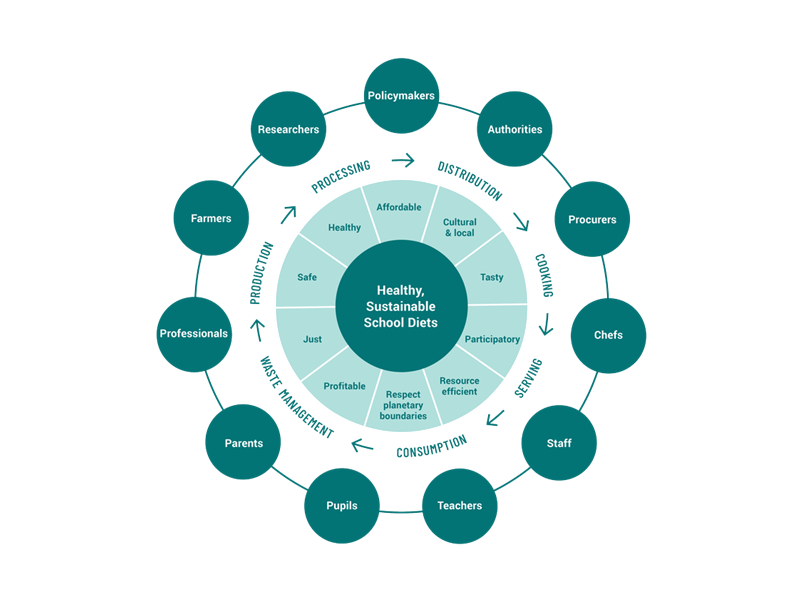
SchoolFood4Change defined the terms “sustainable school food system” (SSFS) and “healthy, sustainable school diets” (HSSD)
These definitions have been missing in scientific discourse. They set the foundation for the entire project methodology, especially the Whole School Food Approach and can be a valuable inspiration for the wider scientific and school food community.
“We believe that defining a healthy and sustainable school environment is essential for achieving a common language among all the actors involved in the food system – both, in and around schools”, says Irene Vidal Sánchez, Technical Project Officer of SF4C at the University of Alcalá in Spain.
Thus, both definitions will facilitate debate and action on improving school meals and therefore also serve to contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals.
Focus on children and adolescents
Even though there was no official definition regarding healthy and sustainable school environments, many organisations had already established definitions for “sustainable food” in their official documents. Other initiatives had also included the term “sustainability” in their development criteria.
However, all previous definitions did not prioritised children and adolescents as key stakeholders. Given their unique susceptibility to actions across the entire food system that adversely impact the diets of young people, the definitions were developed with a focus on schools, children and adolescents.
All SF4C project partners identified the key aspects and principles that make school food healthy and sustainable:
- Nutritional content,
- Vegetarian options,
- Organic food,
- Allergies,
- Local food,
- Resource efficiency (e.g. food and food packaging, waste generation).
In addition, it is considered that the food and school menus have to be sufficient and safe and provide optimal nutritional contents. Furthermore, they must be affordable for schools, parents and municipalities and support the resilience of food systems.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF ACHIEVING A SUSTAINABLE SCHOOL FOOD SYSTEM?
Sustainable school food systems (SSFS) promote the regeneration of natural environments. They minimise negative ecological impacts through the curbing of greenhouse-gas emissions and the promotion of climate actions as well as the reduction of water, land, and energy use. They also stand for the regeneration of these resources as well as for reduction of synthetic chemical pesticides, fertilizers and antibiotics. Sustainable school food systems support biodiversity and ecosystems recovery and halting biodiversity loss. They prevent the generation of waste and promote a circular economy. In addition, SSFS support shorten food supply chains and local economies and have broader social benefits.
For further information you find the full definitions of “Sustainable School Food System” and “School Diets” under Resources – Project Information.